We offer in vitro cytokine release and hazard identification assays to evaluate the potential of a biologic drug to cause a drug-drug interaction (DDI) directly or through cytokine effect on the expression of drug-metabolizing enzymes and/or drug transporters.
Biologic-Small Molecule Drug-Drug Interaction Study
You can now request quotes for our research services on BioIVT.com!
Whether you need a single assay or a complete ADME program, BioIVT’s experts will help design and implement the appropriate studies for your drug and research objectives. View BioIVT’s comprehensive portfolio of ADME research services.
FDA Position: Nonclinical DDI Assessment of Biologics
In recent years, we have seen a shift in pharmaceutical development from small molecule therapeutics to large molecules, also known as biologics. This broad category of drugs includes monoclonal antibodies, hormones, growth factors, enzymes, vaccines, oligonucleotides, and other large molecules.
Some biologic drugs have been shown to cause an inflammatory response, leading to elevated cytokine levels and subsequent cytokine-mediated suppression of drug-metabolizing enzymes such as Cytochrome P450s (CYPs)1. To make sure therapeutic proteins (TP) are evaluated properly for safety before administration to human patients, the FDA released a draft guidance for industry in August 2020 outlining a risk-based approach to evaluating the potential for a TP to cause a drug-drug interaction. The draft is based largely on the finalized guidance for small molecule drugs with modifications to reflect findings from current research focused on cytokine modulation. Additionally, the FDA’s 2020 Final Guidance for Industry, “In Vitro Metabolism- and Transporter- Mediated Drug-Drug Interaction Studies,” recognizes that some biologics need to be evaluated in vitro or in vivo for their potential to alter the disposition of small molecule drugs, particularly if the biologic itself is a cytokine or cytokine modulator.

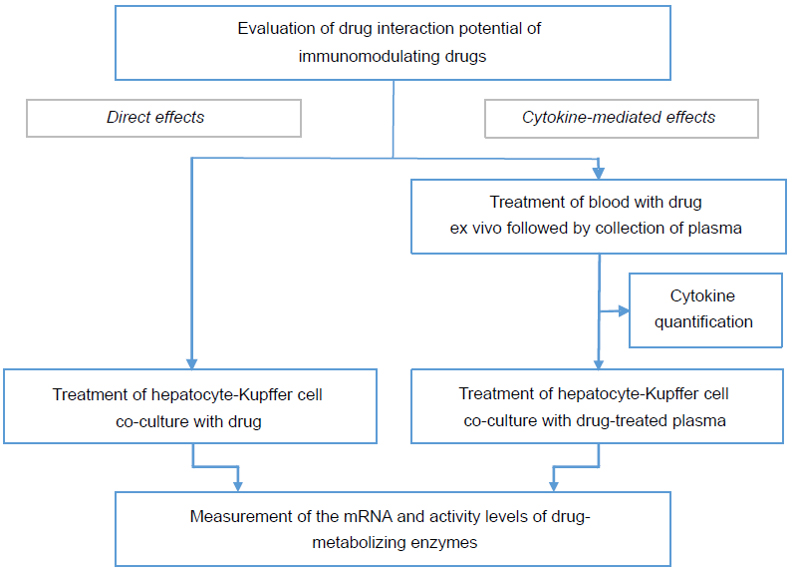
To evaluate a small molecule or biologic drug’s potential to cause a DDI with coadministered small molecule drugs, we offer a study comprising of two assays:
- Cytokine Release
- Hazard Identification
Cytokine Release: Is your therapeutic protein or small molecule drug a cytokine modulator?
It is important to recognize a test article / test biologic’s cytokine modulation potential early in the process of drug development. To evaluate whether or not a drug candidate is a cytokine modulator, we offer a Cytokine Release Assay for both small molecule and biologic drug candidates. In this assay, whole blood is treated with the test article to examine whether it elicits an immune response. The cytokine response in the blood is then quantified in the isolated plasma and compared to an appropriate positive control.
Hazard Identification: Can your drug’s cytokine release response lead to a drug-drug interaction?
For cytokine modulators, we offer a Hazard Identification Study to determine the potential and extent of direct- or cytokine-mediated effects of a test biologic / small molecule drug on CYP enzymes.
- For evaluation of direct effect, co-cultures containing fresh human hepatocytes and Kupffer cells are treated with test biologic / test article
- For evaluation of indirect, cytokine-mediated effect, co-cultures containing fresh human hepatocytes and Kupffer cells are treated with plasma that was isolated from whole blood treated with the drug in a specialized assay designed and patented by XenoTech’s Research & Development team
- Following treatment, CYP enzymatic activity is measured and change in enzyme expression levels is quantified by qRT-PCR analysis
Analysis of assay data allows a drug developer to determine the small molecule drug or test biologic’s potential to cause cytokine release in vivo and then compare the magnitude of response of the drug candidate to known cytokine modulators currently in the clinic.
Scientific Resources Relating to Biologic-Small Molecule Drug-Drug Interaction:
Cytokine-Mediated Suppression of CYP Enzymes By a Toll-like Receptor 9 Agonist in Hepatocytes
Webinar: In Vitro Evaluation of Immunomodulating Drugs as Perpetrators of Drug Interactions
Poster: An in vitro test system to evaluate drug-drug interactions with biologics
See all related content in the Access ADME Scientific Resources portal