Caco-2 Cell Permeability Assay
Our Cell Permeability Assay gives you quick, low-cost data for one or more compounds to better understand permeability properties of drug candidates.
The permeability of a compound can affect its absorption and distribution; our Cell Permeability assay makes it possible to measure permeability across a Caco-2 monolayer to primarily evaluate intestinal absorption. We also offer a definitive cell permeability assay using a MDCKII-MDR1 monolayer to evaluate potential blood-brain barrier permeability. Our flexible assay designs allow you to measure unidirectional or bidirectional permeability, and inhibitors can be added to evaluate the effect transporters have on the permeability of a drug candidate.
Moving quickly through drug discovery and development saves you time and money; get data quickly to make risk-based decisions faster and get you through the pipeline more efficiently.
Our Approach to In Vitro Cell Permeability Studies
- Incubations performed in 24-well transwell plates
- Permeability options include; unidirectional A->B or B->A, bidirectional A->B and B->A, + / – inhibitor
- Options for 1 or 3 incubation time points
- Cultured Caco-2 cells
- Incubations performed in triplicate
- Positive control included
- A tabulated summary of results includes:
- Permeability (Papp)
- % recovery
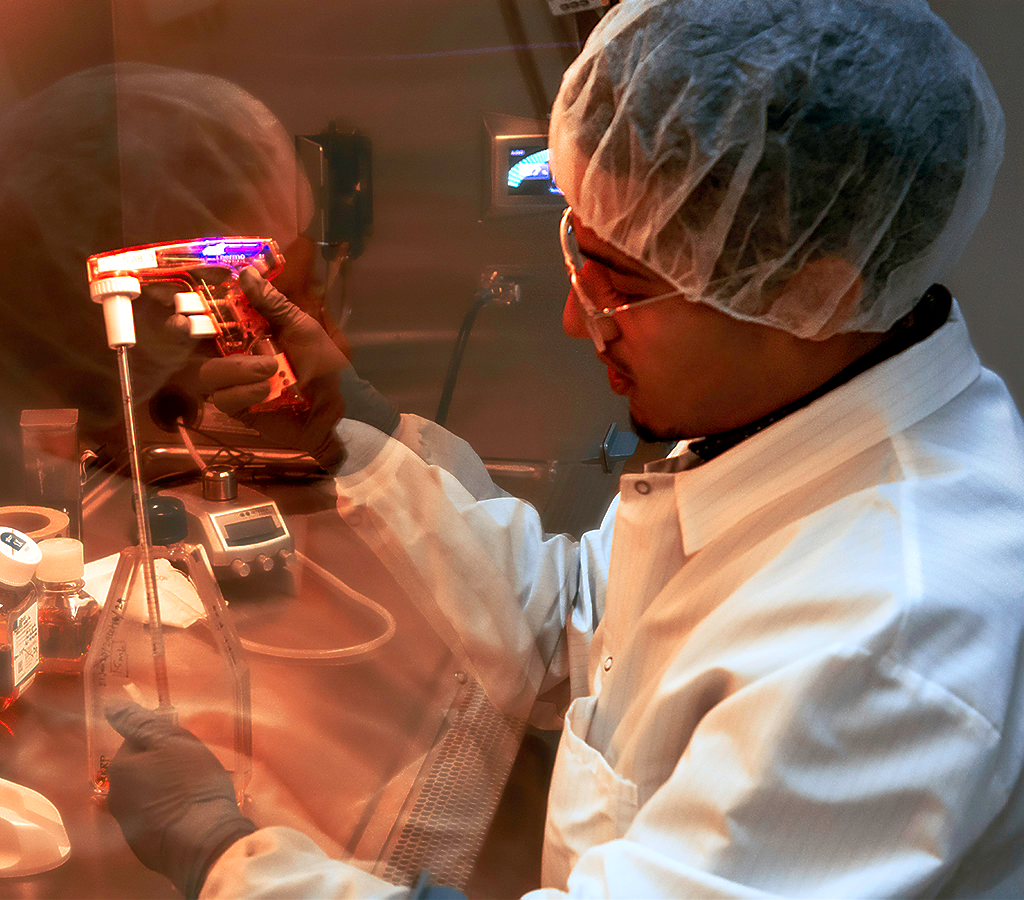

| Cell Line | Positive Control / probe substrate | Positive Control inhibitor | Study Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caco-2 | digoxin | Valspodar | MTS or Definitive |
| MDCKII-MDR1 | digoxin | Valspodar/Verapamil | Definitive Only |
| MDCKII-BCRP | Prazosin | Ko143 | Definitive Only |
Transwell Caco-2 Cell Permeability Assay Design
The design of a MTS Caco-2 cell permeability assay is similar to the design of a P-gp substrate assay. The assay is conducted in a transwell plate, which can be thought of as a cup within a cup with a polarized monolayer of Caco-2 cells grown on a permeable membrane that separates the two compartments. This creates a basal section and an apical section on either side of the monolayer of cells. Test compound is added, either to the apical side or the basal side, and the efflux of the compound in either direction is measured.
In addition to the compound being tested, caffeine and mannitol are also included to serve as a high and low permeability control, respectively. The bidirectional permeability of the test article across the cells is measured in both the apical to basal and basal to apical directions in order to calculate the Papp and efflux ratio. A treatment with a known P-gp specific inhibitor is also included to separate P-gp transport from true membrane permeability of the test compound.